Arduino > BoussoleNumériqueHM55B
Contents (hide)

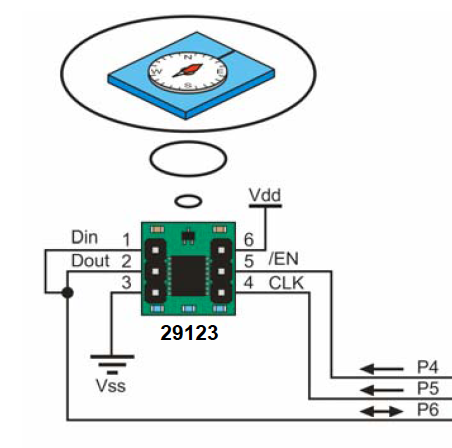
Vdd=5V Vss=GND
1. Exemple ASCII de base
Utiliser un des exemples de la communication série ASCII? pour pouvoir recueillir les données.
Brancher le HM55B à l'Arduino selon le tableau suivant:
| Broche HM55B | Broche Arduino |
| 1 | 6 (numérique) |
| 2 | 6 (numérique) |
| 3 | GND |
| 4 | 5 (numérique) |
| 5 | 4 (numérique) |
| 6 | 5V |
// Based on code by kiilo kiilo@kiilo.org
// found here: http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B
// PINS
#define EN 4
#define CLK 5
#define DIO 6
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
// Setup pins
pinMode(EN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
pinMode(CLK, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
// Reset HM55B
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,0,4);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Start measuring
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,B1000,4);
// Wait till data is ready
int result;
do {
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,B1100,4);
pinMode(DIO, INPUT);
result = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,4);
}
while (result != B1100);
// Data should be ready, read it
int x = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,11);
int y = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,11);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
// The digital compass does not represent negative values the same
// way as does the Arduino does.
// Correct negative values:
if ( x & (1<<10) ) {
x = (B11111000 << 8) | x;
}
if ( y & (1<<10) ) {
y = (B11111000 << 8) | y;
}
// Find the angle
int angle = 180 * (atan2(-1 * y , x) / M_PI);
Serial.println(angle);
}
// Shift functions
void shiftNOut(byte dataPin, byte clockPin, int value, byte n) {
// Send most significant byte out first
int mask = 0x01 << (n-1);
for(byte i = 0; i < n; i++) {
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
if ( value & mask ) {
digitalWrite(dataPin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(dataPin, LOW);
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, HIGH);
mask = mask >> 1;
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
digitalWrite(dataPin, LOW);
}
int shiftNIn(byte dataPin, byte clockPin, byte n) {
int result=0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
digitalWrite(clockPin, HIGH);
__asm__("nop\n\t""nop\n\t"); // Waste time (2 x 62.5 ns)
result= result << 1;
if (digitalRead(dataPin) == HIGH) {
result = result | 0x01;
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
__asm__("nop\n\t""nop\n\t"); // Waste time (2 x 62.5 ns)
}
return result;
}
2. Exemple Tata
Cet exemple utilise Tata.
Brancher le HM55B à l'Arduino en suivant l'exemple précédent.
#include <Tata.h>
/*
This example sends the data read from a HM55B digital compass
to the computer by ASCII:
HM55B > bit shifting > Arduino/Tata > ASCII > computer
To trigger a read of the sensor send the following ASCII message:
"HM55B"
The computer will then receive an ASCII response in the form:
"HM55B x"
where x is the angle measured in degrees
Connect the sensor's /EN pin to the Arduino's digital pin 4
Connect the sensor's CLK pin to the Arduino's digital pin 5
Connect the sensor's Din and Dout pins to the Arduino's digital pin 6
*/
#define EN 4
#define CLK 5
#define DIO 6
byte reading;
void messageReceived() {
if ( Tata.type() == ASCII ) {
if ( Tata.checkWord("HM55B")) {
startReading();
}
}
}
void setup() {
byte digitalPinsDetached[] = {
4,5,6 };
// Tata.begin()'s arguments are:
// 1: baud rate
// 2: custom message function
// 3: custom firmware name
// 4: array of digital pins detached
// 5: number of digital pins detached
// 6: array of analog pins detached
// 7: number of analog pins detached
Tata.begin(57600,messageReceived,"HM55B",digitalPinsDetached,3,0,0);
// Setup pins
pinMode(EN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
pinMode(CLK, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
// Reset HM55B
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,0,4);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
}
void loop() {
Tata.process();
// We check to see if there is any available data
if ( reading ) {
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,B1100,4);
pinMode(DIO, INPUT);
int result = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,4);
// If data is ready
if ( result == B1100 ) {
// Read it
int x = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,11);
int y = shiftNIn(DIO,CLK,11);
digitalWrite(EN,HIGH);
reading = 0;
// The digital compass does not represent negative values the same
// way as does the Arduino does.
// Correct negative values:
if ( x & (1<<10) ) {
x = (B11111000 << 8) | x;
}
if ( y & (1<<10) ) {
y = (B11111000 << 8) | y;
}
// Find the angle
int angle = 180 * (atan2(-1 * y , x) / M_PI);
Serial.print("HM55B ");
Serial.println(angle);
}
}
}
// HM55B
void startReading() {
// Initiate a reading
reading = 1;
digitalWrite(EN,LOW);
pinMode(DIO, OUTPUT);
shiftNOut(DIO,CLK,B1000,4);
}
// SHIFTING
void shiftNOut(byte dataPin, byte clockPin, int value, byte n) {
// Send most significant byte out first
int mask = 0x01 << (n-1);
for(byte i = 0; i < n; i++) {
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
if ( value & mask ) {
digitalWrite(dataPin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(dataPin, LOW);
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, HIGH);
mask = mask >> 1;
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
digitalWrite(dataPin, LOW);
}
int shiftNIn(byte dataPin, byte clockPin, byte n) {
int result=0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
digitalWrite(clockPin, HIGH);
__asm__("nop\n\t""nop\n\t"); // Waste time (2 x 62.5 ns)
result= result << 1;
if (digitalRead(dataPin) == HIGH) {
result = result | 0x01;
}
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
__asm__("nop\n\t""nop\n\t"); // Waste time (2 x 62.5 ns)
}
return result;
}