Arduino > Métronomes et processus parallèles («multi-threading»)
Contents (hide)
1. Métronome
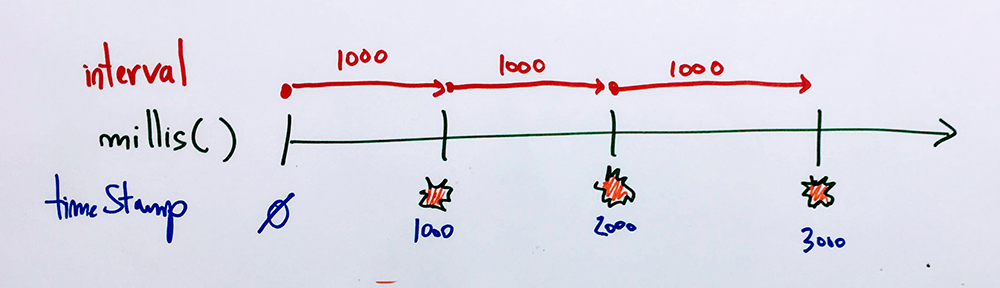
unsigned long timeStamp;
unsigned long interval = 1000;
void setup() {
}
void loop() {
if ( millis() - timeStamp >= interval ) { // SI interval TEMPS S'EST ECOULE DEPUIS LE DERNIER timeStamp
timeStamp = millis(); // ENREGISTRER LE TEMPS COURANT DANS LE timeStamp
/*
FAIRE DE QUOI ICI A CHAQUE INTERVALLE
*/
}
}
2. Tableau d'intervalles
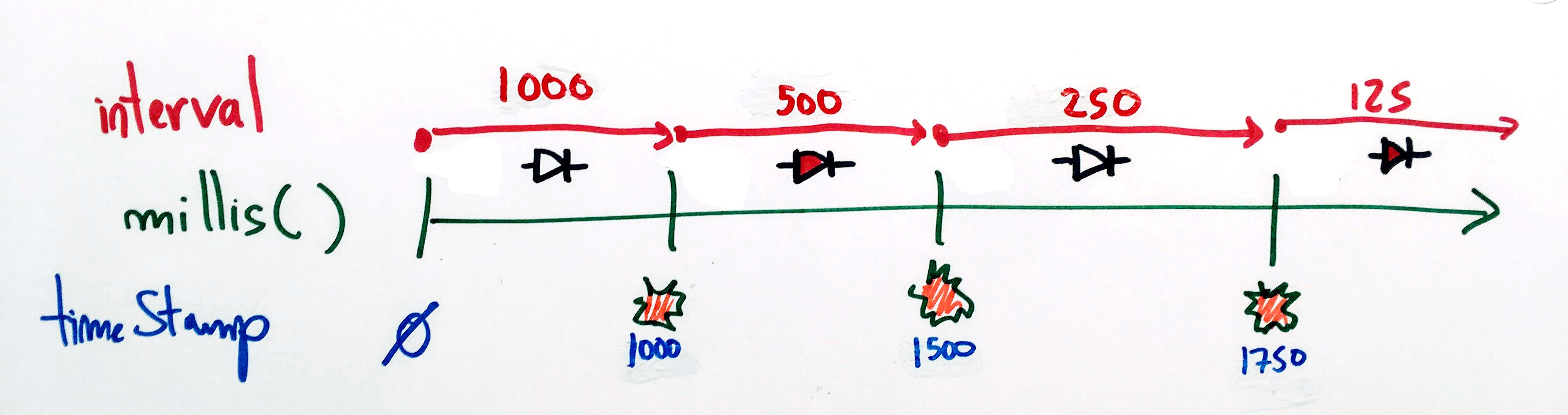
unsigned long timeStamp;
#define TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU 4
unsigned long intervals[TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU] = {1000,500,250,125};
int indexDuTableau = 0;
int ledState = LOW;
void setup() {
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// SI `interval` TEMPS S'EST ECOULE DEPUIS LE DERNIER `timeStamp = millis()`
if ( millis() - timeStamp >= intervals[indexDuTableau] ) {
// ENREGISTRER LE TEMPS COURANT DANS `timeStamp `
timeStamp = millis();
// BASCULER LA DEL
if ( ledState == LOW ) ledState = HIGH;
else ledState = LOW;
// ALLUMER OU ETEINDRE LA DEL
digitalWrite( 13, ledState);
// INCREMENT L'INDEX DU TABLEAU
indexDuTableau = indexDuTableau + 1;
// SI l'INDEX DEPASSE LA TAILLE DU TABLEAU REMETTRE L'INDEX A 0
if ( indexDuTableau >= TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU ) indexDuTableau = 0;
}
}
3. Tableau d'intervalles avec une durée de déclenchement
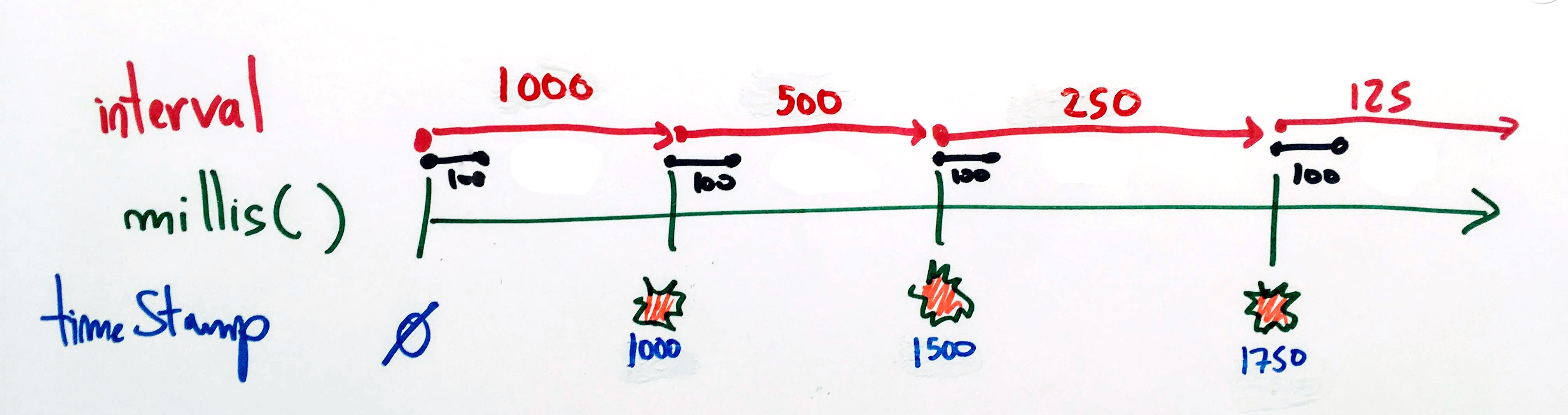
unsigned long timeStamp;
#define TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU 4
unsigned long intervals[TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU] = {1000,500,250,125};
int indexDuTableau = 0;
unsigned long timeStampLed;
unsigned long intervalLed = 100;
void setup() {
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// SI `interval` TEMPS S'EST ECOULE DEPUIS LE DERNIER `timeStamp = millis()`
if ( millis() - timeStamp >= intervals[indexDuTableau] ) {
// ENREGISTRER LE TEMPS COURANT DANS `timeStamp `
timeStamp = millis();
// ALLUMER LA DEL
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
// COMMENCER A COMPTER LE TEMPS POUR LA DEL
timeStampLed = millis();
// INCREMENT L'INDEX DU TABLEAU
indexDuTableau = indexDuTableau + 1;
// SI l'INDEX DEPASSE LA TAILLE DU TABLEAU REMETTRE L'INDEX A 0
if ( indexDuTableau >= TAILLE_DU_TABLEAU ) indexDuTableau = 0;
}
// SI `intervalLed` TEMPS S'EST ECOULE DEPUIS `timeStampLed = millis()`
// ALORS ETEINDRE LA DEL
if ( millis() - timeStampLed >= intervalLed ) {
digitalWrite( 13, LOW);
}
}
4. Clignoter une DEL sans delay()
/* Blink without Delay
Turns on and off a light emitting diode(LED) connected to a digital
pin, without using the delay() function. This means that other code
can run at the same time without being interrupted by the LED code.
The circuit:
* LED attached from pin 13 to ground.
* Note: on most Arduinos, there is already an LED on the board
that's attached to pin 13, so no hardware is needed for this example.
*/
// the number of the LED pin
#define LEDPIN 13
// interval at which to blink (milliseconds)
#define INTERVAL 1000
int ledState = LOW; // ledState used to set the LED
unsigned long timeStamp = 0; // will store last time LED was updated
void setup() {
// set the digital pin as output:
pinMode(LEDPIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// check to see if it's time to blink the LED; that is, if the
// difference between the current time and last time you blinked
// the LED is bigger than the interval at which you want to
// blink the LED.
if(millis() - timeStamp >= INTERVAL) {
// save the last time you blinked the LED
timeStamp = timeStamp + INTERVAL;
// if the LED is off turn it on and vice-versa:
if (ledState == LOW)
ledState = HIGH;
else
ledState = LOW;
// set the LED with the ledState of the variable:
digitalWrite(LEDPIN, ledState);
}
// here is where you'd put code that needs to be running all the time.
}
5. Clignoter deux DEL sans delay()
/*
The circuit:
Attach a red LED to pin 2 (with an appropriate resistor) and
a green LED to pin 3 (with an appropriate resistor).
*/
// the LED pins
#define RED_LED 2
#define GREEN_LED 3
// interval at which to blink (milliseconds)
#define RED_INTERVAL 1000
#define GREEN_INTERVAL 500
int redLedState;
int greenLedState;
unsigned long redTimeStamp;
unsigned long greenTimeStamp;
void setup() {
pinMode(RED_LED,OUTPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_LED,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
if(millis() - redTimeStamp >= RED_INTERVAL ) {
// save the last time you blinked the LED
redTimeStamp = millis();
// if the LED is off turn it on and vice-versa:
if (redLedState == LOW)
redLedState = HIGH;
else
redLedState = LOW;
// set the LED with the ledState of the variable:
digitalWrite(RED_LED, redLedState);
}
if(millis() - greenTimeStamp >= GREEN_INTERVAL ) {
// save the last time you blinked the LED
greenTimeStamp = millis();
// if the LED is off turn it on and vice-versa:
if (greenLedState == LOW)
greenLedState = HIGH;
else
greenLedState = LOW;
// set the LED with the ledState of the variable:
digitalWrite(GREEN_LED, greenLedState);
}
}
6. Avec une classe
/*
Circuit:
Attacher une DEL rouge à la broche 2 (avec une résistance appropriée) et
une DEL verte à la broche 3 (avec une résistance appropriée) .
*/
class Led {
private:
byte pin;
byte state;
int interval;
unsigned long lastMillis;
public:
Led(byte _pin, int _interval) {
pin = _pin;
interval = _interval;
pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);
}
void update() {
if(millis() - lastMillis > interval) {
lastMillis = millis();
if (state == LOW)
state = HIGH;
else
state = LOW;
digitalWrite(pin, state);
}
}
};
Led red(2,1000);
Led green(3,500);
/*
// La ligne suivant démontre comment initialiser des classes dans un tableau:
Led leds[2] = {Led(2,1000), Led(3,500)};
*/
void setup() {
}
void loop()
{
red.update();
green.update();
}