Arduino > Programmateur Arduino ISP
Contents (hide)
1. Introduction
Un Arduino Leonardo peut programmer d'autres microcontrôleurs AVR. Ce est qui surtout utile pour créer des Arduino autonomes.
À noter que la procédure décrite dans cette page fonctionne seulement avec des microcontrôleurs vierges ou qui utilisent l'horloge interne (internal clock). Si le microcontrôleur a été configuré pour utiliser une horloge externe, cette dernière doit être ajoutée au circuit pour pouvoir programmer le microcontrôleur.
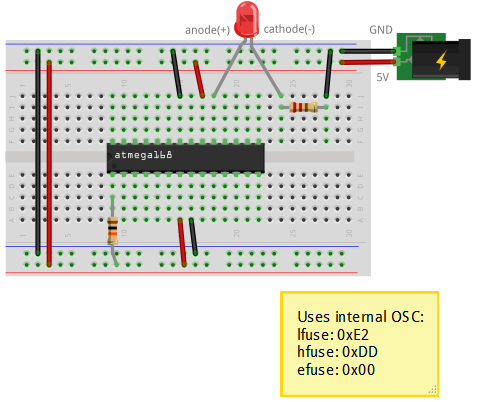
2. Le circuit pour programmer un ATMEGA168 à partir d'un Arduino Leonardo
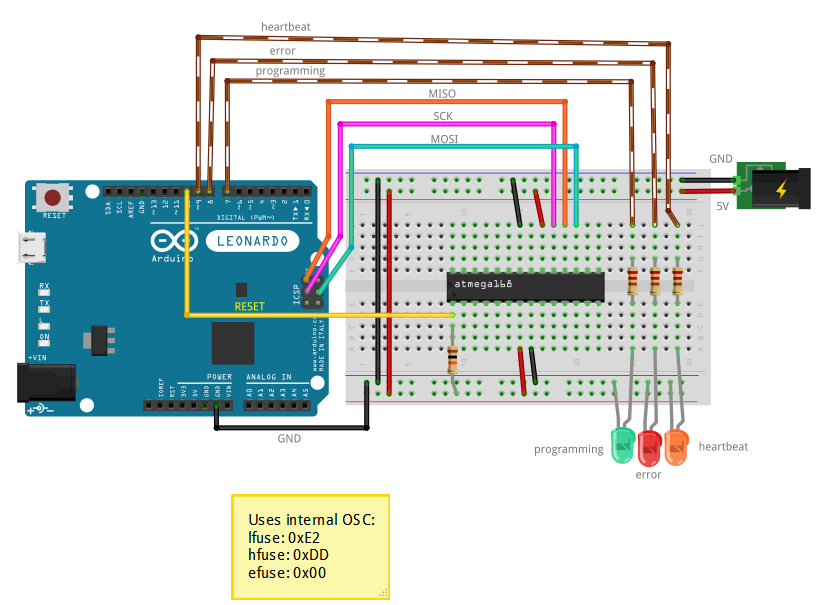
| Leonardo | ATMEGA168 |
| 10 | 1 |
| SCK | SCK |
| MISO | MISO |
| MOSI | MOSI |
| GND | GND |
 |  |
3. Procédure
3.1 Résumé
Initialisation (à faire une seule fois):
- Ajouter les fichiers nécessaires au sketchbook d'Arduino (Documents > Arduino).
- Programmer l'Arduino Leonardo en tant que programmateur ISP (Arduino as ISP (Leonardo)) avec la procédure habituelle de téléversement.
- Changer les «fuses» de l'ATMEGA168 en gravant le «bootloader».
Modification (à répéter chaque fois que vous voulez changer le code de votre Arduino autonome):
- Téléverser «Blink» (ou le code de votre choix) sur le microcontrôleur ATMEGA168 avec votre Arduino Leonardo en tant que programmateur ISP (Arduino as ISP).
- Débrancher l'Arduino Leonardo et installer une DEL et résistance sur votre nouvel Arduino autonome à la broche 13.
3.2 Initialisation
Fermer le logiciel Arduino.
Ajouter ce dossier (tof) au sous-dossier hardware (à créer s'il n'existe pas) du sketchbook d'Arduino (Documents > Arduino > hardware). Au final, le chemin devrait être: Documents > Arduino > hardware > tof
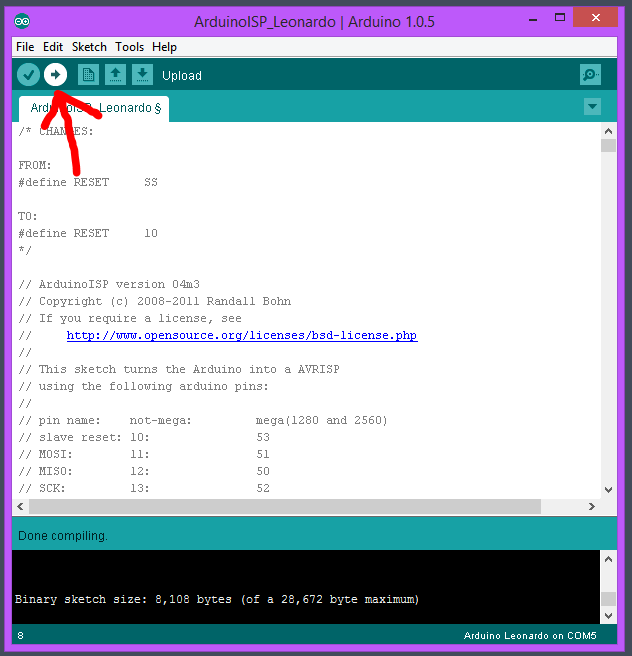
Démarrer le logiciel Arduino et téléverser le code suivant sur l'Arduino Leonardo:
CLIQUER POUR AFFICHER/CACHER LE CODE
/* CHANGES FOR LEONARDO:
FROM:
#define RESET SS
TO:
#define RESET 10
*/
// ArduinoISP version 04m3
// Copyright (c) 2008-2011 Randall Bohn
// If you require a license, see
// http://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php
//
// This sketch turns the Arduino into a AVRISP
// using the following arduino pins:
//
// pin name: not-mega: mega(1280 and 2560)
// slave reset: 10: 53
// MOSI: 11: 51
// MISO: 12: 50
// SCK: 13: 52
//
// Put an LED (with resistor) on the following pins:
// 9: Heartbeat - shows the programmer is running
// 8: Error - Lights up if something goes wrong (use red if that makes sense)
// 7: Programming - In communication with the slave
//
// 23 July 2011 Randall Bohn
// -Address Arduino issue 509 :: Portability of ArduinoISP
// http://code.google.com/p/arduino/issues/detail?id=509
//
// October 2010 by Randall Bohn
// - Write to EEPROM > 256 bytes
// - Better use of LEDs:
// -- Flash LED_PMODE on each flash commit
// -- Flash LED_PMODE while writing EEPROM (both give visual feedback of writing progress)
// - Light LED_ERR whenever we hit a STK_NOSYNC. Turn it off when back in sync.
// - Use pins_arduino.h (should also work on Arduino Mega)
//
// October 2009 by David A. Mellis
// - Added support for the read signature command
//
// February 2009 by Randall Bohn
// - Added support for writing to EEPROM (what took so long?)
// Windows users should consider WinAVR's avrdude instead of the
// avrdude included with Arduino software.
//
// January 2008 by Randall Bohn
// - Thanks to Amplificar for helping me with the STK500 protocol
// - The AVRISP/STK500 (mk I) protocol is used in the arduino bootloader
// - The SPI functions herein were developed for the AVR910_ARD programmer
// - More information at http://code.google.com/p/mega-isp
#include "pins_arduino.h"
#define RESET 10
#define LED_HB 9
#define LED_ERR 8
#define LED_PMODE 7
#define PROG_FLICKER true
#define HWVER 2
#define SWMAJ 1
#define SWMIN 18
// STK Definitions
#define STK_OK 0x10
#define STK_FAILED 0x11
#define STK_UNKNOWN 0x12
#define STK_INSYNC 0x14
#define STK_NOSYNC 0x15
#define CRC_EOP 0x20 //ok it is a space...
void pulse(int pin, int times);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(19200);
pinMode(LED_PMODE, OUTPUT);
pulse(LED_PMODE, 2);
pinMode(LED_ERR, OUTPUT);
pulse(LED_ERR, 2);
pinMode(LED_HB, OUTPUT);
pulse(LED_HB, 2);
}
int error=0;
int pmode=0;
// address for reading and writing, set by 'U' command
int here;
uint8_t buff[256]; // global block storage
#define beget16(addr) (*addr * 256 + *(addr+1) )
typedef struct param {
uint8_t devicecode;
uint8_t revision;
uint8_t progtype;
uint8_t parmode;
uint8_t polling;
uint8_t selftimed;
uint8_t lockbytes;
uint8_t fusebytes;
int flashpoll;
int eeprompoll;
int pagesize;
int eepromsize;
int flashsize;
}
parameter;
parameter param;
// this provides a heartbeat on pin 9, so you can tell the software is running.
uint8_t hbval=128;
int8_t hbdelta=8;
void heartbeat() {
if (hbval > 192) hbdelta = -hbdelta;
if (hbval < 32) hbdelta = -hbdelta;
hbval += hbdelta;
analogWrite(LED_HB, hbval);
delay(20);
}
void loop(void) {
// is pmode active?
if (pmode) digitalWrite(LED_PMODE, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(LED_PMODE, LOW);
// is there an error?
if (error) digitalWrite(LED_ERR, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(LED_ERR, LOW);
// light the heartbeat LED
heartbeat();
if (Serial.available()) {
avrisp();
}
}
uint8_t getch() {
while(!Serial.available());
return Serial.read();
}
void fill(int n) {
for (int x = 0; x < n; x++) {
buff[x] = getch();
}
}
#define PTIME 30
void pulse(int pin, int times) {
do {
digitalWrite(pin, HIGH);
delay(PTIME);
digitalWrite(pin, LOW);
delay(PTIME);
}
while (times--);
}
void prog_lamp(int state) {
if (PROG_FLICKER)
digitalWrite(LED_PMODE, state);
}
void spi_init() {
uint8_t x;
SPCR = 0x53;
x=SPSR;
x=SPDR;
}
void spi_wait() {
do {
}
while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF)));
}
uint8_t spi_send(uint8_t b) {
uint8_t reply;
SPDR=b;
spi_wait();
reply = SPDR;
return reply;
}
uint8_t spi_transaction(uint8_t a, uint8_t b, uint8_t c, uint8_t d) {
uint8_t n;
spi_send(a);
n=spi_send(b);
//if (n != a) error = -1;
n=spi_send(c);
return spi_send(d);
}
void empty_reply() {
if (CRC_EOP == getch()) {
Serial.print((char)STK_INSYNC);
Serial.print((char)STK_OK);
}
else {
error++;
Serial.print((char)STK_NOSYNC);
}
}
void breply(uint8_t b) {
if (CRC_EOP == getch()) {
Serial.print((char)STK_INSYNC);
Serial.print((char)b);
Serial.print((char)STK_OK);
}
else {
error++;
Serial.print((char)STK_NOSYNC);
}
}
void get_version(uint8_t c) {
switch(c) {
case 0x80:
breply(HWVER);
break;
case 0x81:
breply(SWMAJ);
break;
case 0x82:
breply(SWMIN);
break;
case 0x93:
breply('S'); // serial programmer
break;
default:
breply(0);
}
}
void set_parameters() {
// call this after reading paramter packet into buff[]
param.devicecode = buff[0];
param.revision = buff[1];
param.progtype = buff[2];
param.parmode = buff[3];
param.polling = buff[4];
param.selftimed = buff[5];
param.lockbytes = buff[6];
param.fusebytes = buff[7];
param.flashpoll = buff[8];
// ignore buff[9] (= buff[8])
// following are 16 bits (big endian)
param.eeprompoll = beget16(&buff[10]);
param.pagesize = beget16(&buff[12]);
param.eepromsize = beget16(&buff[14]);
// 32 bits flashsize (big endian)
param.flashsize = buff[16] * 0x01000000
+ buff[17] * 0x00010000
+ buff[18] * 0x00000100
+ buff[19];
}
void start_pmode() {
spi_init();
// following delays may not work on all targets...
pinMode(RESET, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RESET, HIGH);
pinMode(SCK, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SCK, LOW);
delay(50);
digitalWrite(RESET, LOW);
delay(50);
pinMode(MISO, INPUT);
pinMode(MOSI, OUTPUT);
spi_transaction(0xAC, 0x53, 0x00, 0x00);
pmode = 1;
}
void end_pmode() {
pinMode(MISO, INPUT);
pinMode(MOSI, INPUT);
pinMode(SCK, INPUT);
pinMode(RESET, INPUT);
pmode = 0;
}
void universal() {
int w;
uint8_t ch;
fill(4);
ch = spi_transaction(buff[0], buff[1], buff[2], buff[3]);
breply(ch);
}
void flash(uint8_t hilo, int addr, uint8_t data) {
spi_transaction(0x40+8*hilo,
addr>>8 & 0xFF,
addr & 0xFF,
data);
}
void commit(int addr) {
if (PROG_FLICKER) prog_lamp(LOW);
spi_transaction(0x4C, (addr >> 8) & 0xFF, addr & 0xFF, 0);
if (PROG_FLICKER) {
delay(PTIME);
prog_lamp(HIGH);
}
}
//#define _current_page(x) (here & 0xFFFFE0)
int current_page(int addr) {
if (param.pagesize == 32) return here & 0xFFFFFFF0;
if (param.pagesize == 64) return here & 0xFFFFFFE0;
if (param.pagesize == 128) return here & 0xFFFFFFC0;
if (param.pagesize == 256) return here & 0xFFFFFF80;
return here;
}
void write_flash(int length) {
fill(length);
if (CRC_EOP == getch()) {
Serial.print((char) STK_INSYNC);
Serial.print((char) write_flash_pages(length));
}
else {
error++;
Serial.print((char) STK_NOSYNC);
}
}
uint8_t write_flash_pages(int length) {
int x = 0;
int page = current_page(here);
while (x < length) {
if (page != current_page(here)) {
commit(page);
page = current_page(here);
}
flash(LOW, here, buff[x++]);
flash(HIGH, here, buff[x++]);
here++;
}
commit(page);
return STK_OK;
}
#define EECHUNK (32)
uint8_t write_eeprom(int length) {
// here is a word address, get the byte address
int start = here * 2;
int remaining = length;
if (length > param.eepromsize) {
error++;
return STK_FAILED;
}
while (remaining > EECHUNK) {
write_eeprom_chunk(start, EECHUNK);
start += EECHUNK;
remaining -= EECHUNK;
}
write_eeprom_chunk(start, remaining);
return STK_OK;
}
// write (length) bytes, (start) is a byte address
uint8_t write_eeprom_chunk(int start, int length) {
// this writes byte-by-byte,
// page writing may be faster (4 bytes at a time)
fill(length);
prog_lamp(LOW);
for (int x = 0; x < length; x++) {
int addr = start+x;
spi_transaction(0xC0, (addr>>8) & 0xFF, addr & 0xFF, buff[x]);
delay(45);
}
prog_lamp(HIGH);
return STK_OK;
}
void program_page() {
char result = (char) STK_FAILED;
int length = 256 * getch();
length += getch();
char memtype = getch();
// flash memory @here, (length) bytes
if (memtype == 'F') {
write_flash(length);
return;
}
if (memtype == 'E') {
result = (char)write_eeprom(length);
if (CRC_EOP == getch()) {
Serial.print((char) STK_INSYNC);
Serial.print(result);
}
else {
error++;
Serial.print((char) STK_NOSYNC);
}
return;
}
Serial.print((char)STK_FAILED);
return;
}
uint8_t flash_read(uint8_t hilo, int addr) {
return spi_transaction(0x20 + hilo * 8,
(addr >> 8) & 0xFF,
addr & 0xFF,
0);
}
char flash_read_page(int length) {
for (int x = 0; x < length; x+=2) {
uint8_t low = flash_read(LOW, here);
Serial.print((char) low);
uint8_t high = flash_read(HIGH, here);
Serial.print((char) high);
here++;
}
return STK_OK;
}
char eeprom_read_page(int length) {
// here again we have a word address
int start = here * 2;
for (int x = 0; x < length; x++) {
int addr = start + x;
uint8_t ee = spi_transaction(0xA0, (addr >> 8) & 0xFF, addr & 0xFF, 0xFF);
Serial.print((char) ee);
}
return STK_OK;
}
void read_page() {
char result = (char)STK_FAILED;
int length = 256 * getch();
length += getch();
char memtype = getch();
if (CRC_EOP != getch()) {
error++;
Serial.print((char) STK_NOSYNC);
return;
}
Serial.print((char) STK_INSYNC);
if (memtype == 'F') result = flash_read_page(length);
if (memtype == 'E') result = eeprom_read_page(length);
Serial.print(result);
return;
}
void read_signature() {
if (CRC_EOP != getch()) {
error++;
Serial.print((char) STK_NOSYNC);
return;
}
Serial.print((char) STK_INSYNC);
uint8_t high = spi_transaction(0x30, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00);
Serial.print((char) high);
uint8_t middle = spi_transaction(0x30, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00);
Serial.print((char) middle);
uint8_t low = spi_transaction(0x30, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00);
Serial.print((char) low);
Serial.print((char) STK_OK);
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////////////
int avrisp() {
uint8_t data, low, high;
uint8_t ch = getch();
switch (ch) {
case '0': // signon
error = 0;
empty_reply();
break;
case '1':
if (getch() == CRC_EOP) {
Serial.print((char) STK_INSYNC);
Serial.print("AVR ISP");
Serial.print((char) STK_OK);
}
break;
case 'A':
get_version(getch());
break;
case 'B':
fill(20);
set_parameters();
empty_reply();
break;
case 'E': // extended parameters - ignore for now
fill(5);
empty_reply();
break;
case 'P':
start_pmode();
empty_reply();
break;
case 'U': // set address (word)
here = getch();
here += 256 * getch();
empty_reply();
break;
case 0x60: //STK_PROG_FLASH
low = getch();
high = getch();
empty_reply();
break;
case 0x61: //STK_PROG_DATA
data = getch();
empty_reply();
break;
case 0x64: //STK_PROG_PAGE
program_page();
break;
case 0x74: //STK_READ_PAGE 't'
read_page();
break;
case 'V': //0x56
universal();
break;
case 'Q': //0x51
error=0;
end_pmode();
empty_reply();
break;
case 0x75: //STK_READ_SIGN 'u'
read_signature();
break;
// expecting a command, not CRC_EOP
// this is how we can get back in sync
case CRC_EOP:
error++;
Serial.print((char) STK_NOSYNC);
break;
// anything else we will return STK_UNKNOWN
default:
error++;
if (CRC_EOP == getch())
Serial.print((char)STK_UNKNOWN);
else
Serial.print((char)STK_NOSYNC);
}
}
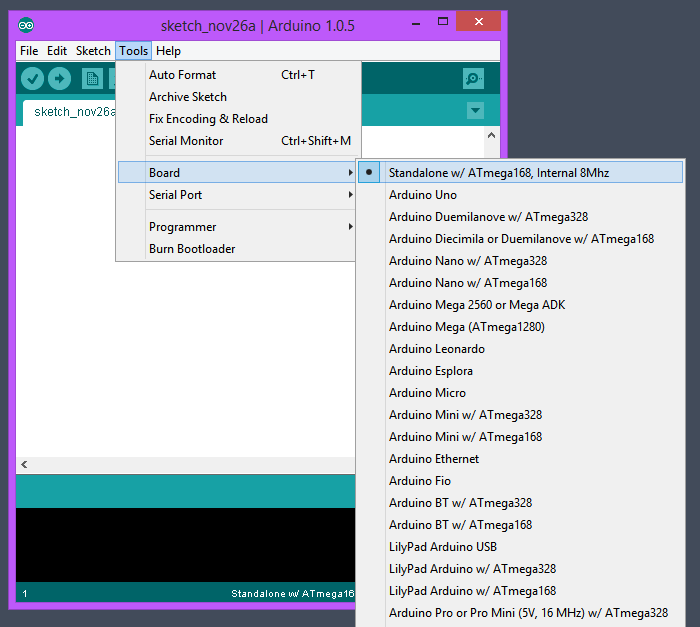
Chosir Standalone w/ ATmega168, Internal 8Mhz dans le menu Tools > Board:
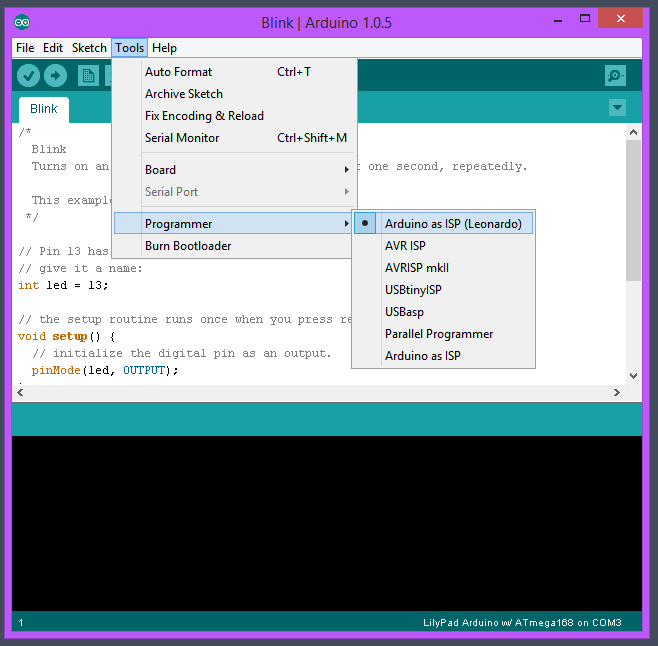
Choisir Arduino as ISP (Leonardo) en tant que programmateur et vérifier que le port du Leonardo est encore sélectionné:
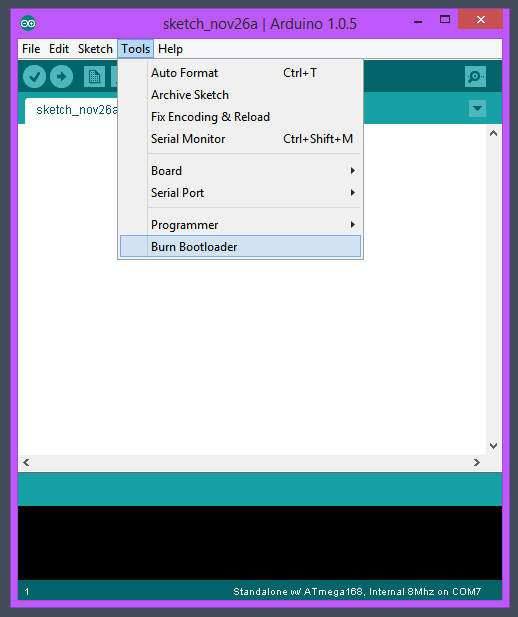
Téléverser le «bootloader»:
3.3 Modification
Chosir Standalone w/ ATmega168, Internal 8Mhz dans le menu Tools > Board:

Choisir Arduino as ISP (Leonardo) en tant que programmateur et vérifier que le port du Leonardo est encore sélectionné:

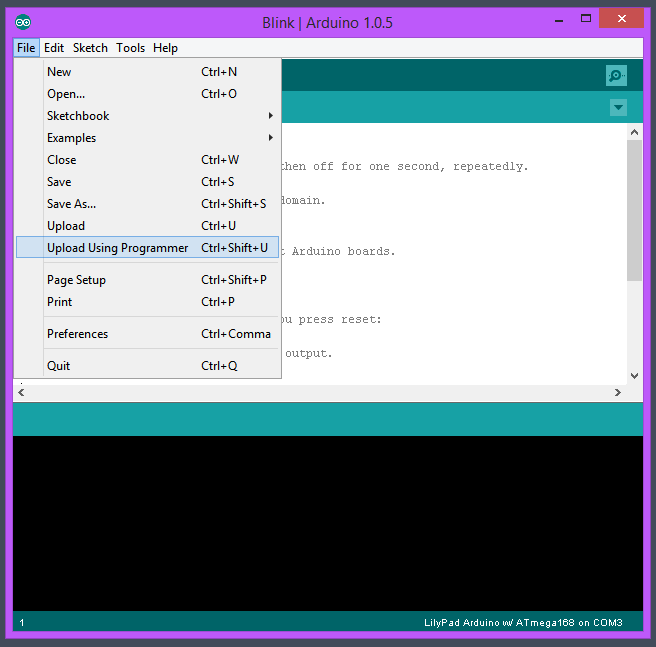
Ouvrir l'exemple Blink (ou tout autre code de votre choix) et le téléverser sur l'Arduino avec le menu File > Upload using programmer:
Vous pouvez maintenant retirer le programmateur et installer une DEL sur la broche Arduino 13: