Tata > SYSEX
Sysex ne supporte que des 7bits. Chaque donnée envoyée doit donc se trouver entre les valeurs 0 et 127.
Tata peut envoyer et recevoir des messages sysex qui contiennent jusqu'à 129 7bits.
Dans tous les exemples suivants:
- Téléchargez le code Arduino sur l'Arduino
- Démarrez TataOSC
- Ouvir le code dans l'application client (Max, Processing, etc)
Exemple simple
Code Arduino:
#include <Tata.h>
/*
This example controls the pwm of a LED connected to pin 9
with a sysex command:
Computer > sysex > Arduino/Tata > PWM > Pin 9
Sysex only supports 7bits so the data will be in the
range of 0 to 127.
Send the following sysex message:
"0 PWM "
Where:
- 0 is a fixed identifier
- PWM is a value in the range of 0 to 127
*/
// HARDWARE CONNECTIONS
int LED = 9;
void messageReceived() {
if ( Tata.type() == SYSEX ) {
byte first7bit = Tata.sysexRead();
// The first sysex 7bit should always be 0.
// This number declares the message as a custom sysex message.
// Other numbers might be reserved by Tata.
// Also check if there is enough data available.
if ( first7bit == 0 && Tata.available() > 0 ) {
byte data = Tata.sysexRead();
// Sysex data travels in 7bits (values are between 0 and 127)
// so we multiply the data by 2 to be in 0 to 254 range of PWM
analogWrite(LED,data*2);
}
}
}
void setup() {
Tata.begin(57600,messageReceived,"PWM");
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
Tata.process();
}
Code Max:

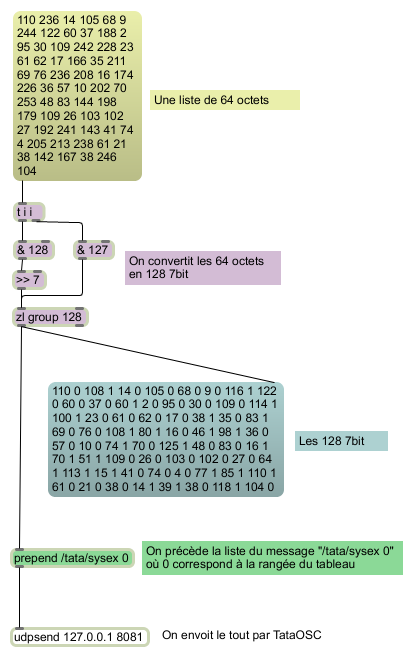
Exemple avec un tableau à deux dimensions
Code Arduino:
#include <Tata.h>
/*
This example receives sysex data that fills up a two dimensional
arrays of 3 rows x 64 columns of bytes:
byte array[3][64];
Computer > sysex > Arduino/Tata > array
Sysex only supports 7bits so the data will be in the
range of 0 to 127.
Tata can support up to 129 7bits per sysex message.
To convert the 7bits into bytes, we add together
two consecutive 7bits as so:
byte b = first 7bit + (second 7bit << 7);
To set the data into the array send the following sysex message:
"# DATA... "
Where:
- # is the row number. In this example 0,1 or 2.
- DATA... is a series of 128 7bits that will fill the columns of
the matching row
*/
// The array
byte array[3][64];
void messageReceived() {
if ( Tata.type() == SYSEX ) {
byte first7bit = Tata.sysexRead();
int size = Tata.available();
if ( first7bit < 3 && size > 0 ) {
byte b;
for ( int i=0; i < size; i++) {
byte new7bit = Tata.sysexRead();
// The following line determines if we are working with an
// odd or even index
if ( i % 2 ) {
// odd: we add the previous and new 7bits to create the
// byte and then set it in the array
b = b + (new7bit << 7);
array[first7bit][i/2] = b;
}
else {
// even: we store the 7bit temporarly
b = new7bit;
}
}
}
/* The commented code is only for testing purposes
else if ( first7bit < 3) {
byte b;
Tata.sysexStart(first7bit);
for ( int i=0; i < 64; i++) {
b = array[first7bit][i];
Tata.sysexWrite(b & B01111111);
Tata.sysexWrite((b & B10000000)>>7);
}
Tata.sysexEnd();
}
*/
}
}
void setup() {
Tata.begin(57600,messageReceived,"sysex_array");
}
void loop() {
Tata.process();
}
Code Max: