Arduino > Rainbowduino
Contents (hide)

Permet de contrôler des matrices de DEL par I2C.
1. Télécharger le micrologiciel sur le Rainbowduino
1.1 Méthode avec un convertisseur USB vers série?
|
Broche du convertisseur USB vers série |
Broche du Rainbowduino |
|
DTR |
DTR |
|
RXD |
TXD |
|
TXD |
RXD |
|
5V |
VCC |
|
GND |
GND |
1.2 Méthode avec un Arduino lobotomisé?
|
Broche de l'Arduino lobotomisé |
Broche du Rainbowduino |
|
RESET |
DTR |
|
RXD |
RXD |
|
TXD |
TXD |
|
5V |
VCC |
|
GND |
GND |
2. Branchement I2C
|
Broche de l'Arduino maître |
Broche du Rainbowduino esclave |
|
Analog 4 |
SDA |
|
Analog 5 |
SCL |
|
5V |
VCC du terminal vert |
|
GND |
GND du terminal vert |
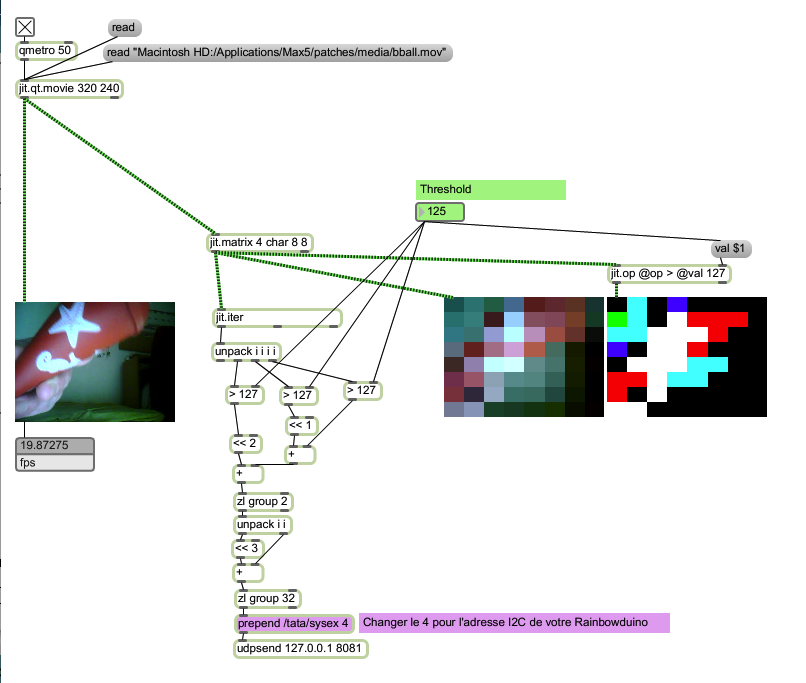
3. Exemple
3.1 Code Arduino maître
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
}
void loop() {
while ( fourTenAvailable() ) {
int channel = fourTenReadChannel();
if ( channel == 13 ) {
Wire.beginTransmission( fourTenReadData() );
}
else if ( channel == 15) {
Wire.endTransmission();
}
else if (channel == 14) {
Wire.write( fourTenReadData() );
}
}
}
//fourTenStart
/*
______ _______
| ____| |__ __|
| |__ ___ _ _ _ __| | ___ _ __
| __/ _ \| | | | '__| |/ _ \ '_ \
| | | (_) | |_| | | | | __/ | | |
|_| \___/ \__,_|_| |_|\___|_| |_|
Description
=============
FourTen est un protocole de communication tres simple et tres rapide.
Il permet d'envoyer des données dont la valeur se situe entre 0 et 1023 (10 bits)
sur 16 canaux numerotes de 0 a 15 (4 bits).
Installation
=============
Pour utiliser le protocole dans Arduino ou Wiring,
copier tout ce qui se trouve entre //fourTenStart et //fourTenEnd
et l'ajouter a la fin de votre sketch.
Utilisation
=============
# fourTenWrite(int canal, int donnee)
Permet d'envoyer un message fourTen.
# fourTenAvailable()
Retourne 1 si un message FourTen est disponible.
Retourne 0 sinon.
# int fourTenReadChannel()
Retourne le canal d'un message FourTen recu.
# int fourTenReadData()
Retourne la donnee d'un message FourTen recu.
Details du protocol FourTen
=============
Chaque message est construit a partir de deux octets:
octet 1 octet 2
bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 - 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
fonction 1 C C C C D D D 0 D D D D D D D
C: canal
D: donnee
octet 1:
bit 7 = 1
bits 6-3 = canal
bits 2-0 = bits 9-7 de la donnee
octet 2:
bit 7 = 0
bits 6-0 = bits 6-0 de la donnee
Le bit 7 de chaque octet sert a identifier si c'est
l'octet 1 ou 2. En excluant ces deux bits,
il reste donc 14 bits qui se subdivisent ainsi:
4 bits (canal) suivis de 10 bits (donnee)
Le canal peut avoir une valeur entre 0-15.
La donnee peut avoir une valeur entre 0-1023.
*/
void fourTenWrite(int channel, int data) {
Serial.write( ( channel << 3 | ( ( data >> 7) & 0x07 ) ) | 0x80);
Serial.write( data & 0x7F);
}
int fourTenBuffer;
int fourTenAvailable( ) {
while ( Serial.available() ) {
int data = Serial.read();
if ( data & 0x80 ) {
fourTenBuffer = data & 0x7F;
}
else {
fourTenBuffer = ( fourTenBuffer << 7 ) | ( data & 0x7F );
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int fourTenReadChannel() {
return fourTenBuffer>>10;
}
int fourTenReadData() {
return fourTenBuffer & 0x3FF;
}
//fourTenEnd
3.2 Code Rainbowduino esclave
#include <Wire.h>
// Change the following line to change your Rainbowduino I2C address
#define I2C_ADDRESS 4
#ifndef Rainbow_h
#define Rainbow_h
//=============================================
//MBI5168
#define SH_DIR_OE DDRC
#define SH_DIR_SDI DDRC
#define SH_DIR_CLK DDRC
#define SH_DIR_LE DDRC
#define SH_BIT_OE 0x08
#define SH_BIT_SDI 0x01
#define SH_BIT_CLK 0x02
#define SH_BIT_LE 0x04
#define SH_PORT_OE PORTC
#define SH_PORT_SDI PORTC
#define SH_PORT_CLK PORTC
#define SH_PORT_LE PORTC
//============================================
#define clk_rising {SH_PORT_CLK&=~SH_BIT_CLK;SH_PORT_CLK|=SH_BIT_CLK;}
#define le_high {SH_PORT_LE|=SH_BIT_LE;}
#define le_low {SH_PORT_LE&=~SH_BIT_LE;}
#define enable_oe {SH_PORT_OE&=~SH_BIT_OE;}
#define disable_oe {SH_PORT_OE|=SH_BIT_OE;}
#define shift_data_1 {SH_PORT_SDI|=SH_BIT_SDI;}
#define shift_data_0 {SH_PORT_SDI&=~SH_BIT_SDI;}
//============================================
#define open_line0 {PORTB=0x04;}
#define open_line1 {PORTB=0x02;}
#define open_line2 {PORTB=0x01;}
#define open_line3 {PORTD=0x80;}
#define open_line4 {PORTD=0x40;}
#define open_line5 {PORTD=0x20;}
#define open_line6 {PORTD=0x10;}
#define open_line7 {PORTD=0x08;}
#define close_all_line {PORTD&=~0xf8;PORTB&=~0x07;}
//============================================
#define CheckRequest (g8Flag1&0x01)
#define SetRequest (g8Flag1|=0x01)
#define ClrRequest (g8Flag1&=~0x01)
//==============================================
#define waitingcmd 0x00
#define processing 0x01
#define checking 0x02
#define showPrefabnicatel 0x01
#define showChar 0x02
#define showColor 0x03
#endif
//=============================================================
unsigned char dots_color[2][3][8][4]; //define Two Buffs (one for Display ,the other for receive data)
//define the Gamma value for correct the different LED matrix
unsigned char GamaTab[16]=
{0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7,0xE7};
//=============================================================
unsigned char line,level;
unsigned char Buffprt=0;
//unsigned char State=0;
unsigned char g8Flag1;
//unsigned char RainbowCMD[5]={0,0,0,0,0};
void setup()
{
//Serial.begin(57600);
//Serial.println("START");
DDRD=0xff;
DDRC=0xff;
DDRB=0xff;
PORTD=0;
PORTB=0;
Wire.begin(I2C_ADDRESS); // join i2c bus
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // define the receive function for receiving data from master
//Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // define the request function for the request from maseter
init_timer2(); // initial the timer for scanning the LED matrix
}
void receiveEvent(int howMany)
{
// unsigned char header = Wire.receive();
//Serial.println(header,DEC);
//if ( header == 32 ) {
unsigned char i = 0;
while(Wire.available()>0) {
unsigned char d = Wire.receive();
// Serial.println(d,DEC);
unsigned char x = i / 4;
unsigned char y = i % 4;
// dots_color[2][3][8][4];
// d = xxRGBRGB // xx(RGB n)(RGB n+1)
dots_color[Buffprt][1][x][y] = ((d & B00100000) ? B11110000 : B00000000) | ((d & B00000100) ? B00001111 : B00000000);
dots_color[Buffprt][0][x][y] = ((d & B00010000) ? B11110000 : B00000000) | ((d & B00000010) ? B00001111 : B00000000);
dots_color[Buffprt][2][x][y] = ((d & B00001000) ? B11110000 : B00000000) | ((d & B00000001) ? B00001111 : B00000000);
i++;
}
//Buffprt = (Buffprt + 1) % 2;
//}
}
void loop() {
}
ISR(TIMER2_OVF_vect) //Timer2 Service
{
TCNT2 = GamaTab[level]; // Reset a scanning time by gamma value table
flash_next_line(line,level); // sacan the next line in LED matrix level by level.
line++;
if(line>7) // when have scaned all LEC the back to line 0 and add the level
{
line=0;
level++;
if(level>15) level=0;
}
}
void init_timer2(void)
{
TCCR2A |= (1 << WGM21) | (1 << WGM20);
TCCR2B |= (1<<CS22); // by clk/64
TCCR2B &= ~((1<<CS21) | (1<<CS20)); // by clk/64
TCCR2B &= ~((1<<WGM21) | (1<<WGM20)); // Use normal mode
ASSR |= (0<<AS2); // Use internal clock - external clock not used in Arduino
TIMSK2 |= (1<<TOIE2) | (0<<OCIE2B); //Timer2 Overflow Interrupt Enable
TCNT2 = GamaTab[0];
sei();
}
//==============================================================
void shift_1_bit(unsigned char LS) //shift 1 bit of 1 Byte color data into Shift register by clock
{
if(LS)
{
shift_data_1;
}
else
{
shift_data_0;
}
clk_rising;
}
//==============================================================
void flash_next_line(unsigned char line,unsigned char level) // scan one line
{
disable_oe;
close_all_line;
open_line(line);
shift_24_bit(line,level);
enable_oe;
}
//==============================================================
void shift_24_bit(unsigned char line,unsigned char level) // display one line by the color level in buff
{
unsigned char color=0,row=0;
unsigned char data0=0,data1=0;
le_high;
for(color=0;color<3;color++)//GBR
{
for(row=0;row<4;row++)
{
data1=dots_color[Buffprt][color][line][row]&0x0f;
data0=dots_color[Buffprt][color][line][row]>>4;
if(data0>level) //gray scale,0x0f aways light
{
shift_1_bit(1);
}
else
{
shift_1_bit(0);
}
if(data1>level)
{
shift_1_bit(1);
}
else
{
shift_1_bit(0);
}
}
}
le_low;
}
//==============================================================
void open_line(unsigned char line) // open the scaning line
{
switch(line)
{
case 0:
{
open_line0;
break;
}
case 1:
{
open_line1;
break;
}
case 2:
{
open_line2;
break;
}
case 3:
{
open_line3;
break;
}
case 4:
{
open_line4;
break;
}
case 5:
{
open_line5;
break;
}
case 6:
{
open_line6;
break;
}
case 7:
{
open_line7;
break;
}
}
}